How are W-2s and final pay stubs different?
You may notice that the gross (before tax) amount on your final pay stub of the year is different from the amount on your W-2. There are three reasons this can occur:
- Your earnings included nontaxable income.
Examples of nontaxable income include reimbursements for mileage or other nontaxable expenses that were paid back to you during a pay period. In this case, the gross wages on your pay stub will often differ from the W-2 wages you see in boxes 1, 3, 5 and 16, because these nontaxable items lower gross taxable wages.
For example: Pat’s gross wages are $34,000. Over the course of the year, Penn State Health reimbursed them $2,000 toward a nontaxed mileage allowance. Because $34,000 – $2,000 = $32,000, Pat’s taxable W-2 wages will be $32,000.
- You participated in a Penn State Health retirement plan.
Retirement plans, like a 401(k), will affect your taxable federal and state wages only. You’ll see these in boxes 1 and 16 on your W-2.
For example: Sally’s gross wages are $40,000, but she contributed $4,000 toward her 401(k) retirement plan for the year. Because $40,000 – $4,000 = $36,000, Sally’s taxable federal and state W-2 wages will be $36,000.
- Penn State Health offers health insurance as a pre-tax deduction.
This is the most common reason for your pay stub earnings to be different from your W-2. If you participated in Penn State Health’s pre-tax health insurance plan, then the taxable wages in your W-2 boxes 1, 3, 5 and 16 will be lower than the amount of the pre-tax health insurance deduction. Pre-tax deductions will lower your gross wages by the annual amount of the deduction.
For example: Dave’s gross wages are $35,000, but he contributed $2,000 to a pre-tax health insurance deduction for the year. Because $35,000 – $2,000 = $33,000, Dave’s taxable W-2 wages will be $33,000.
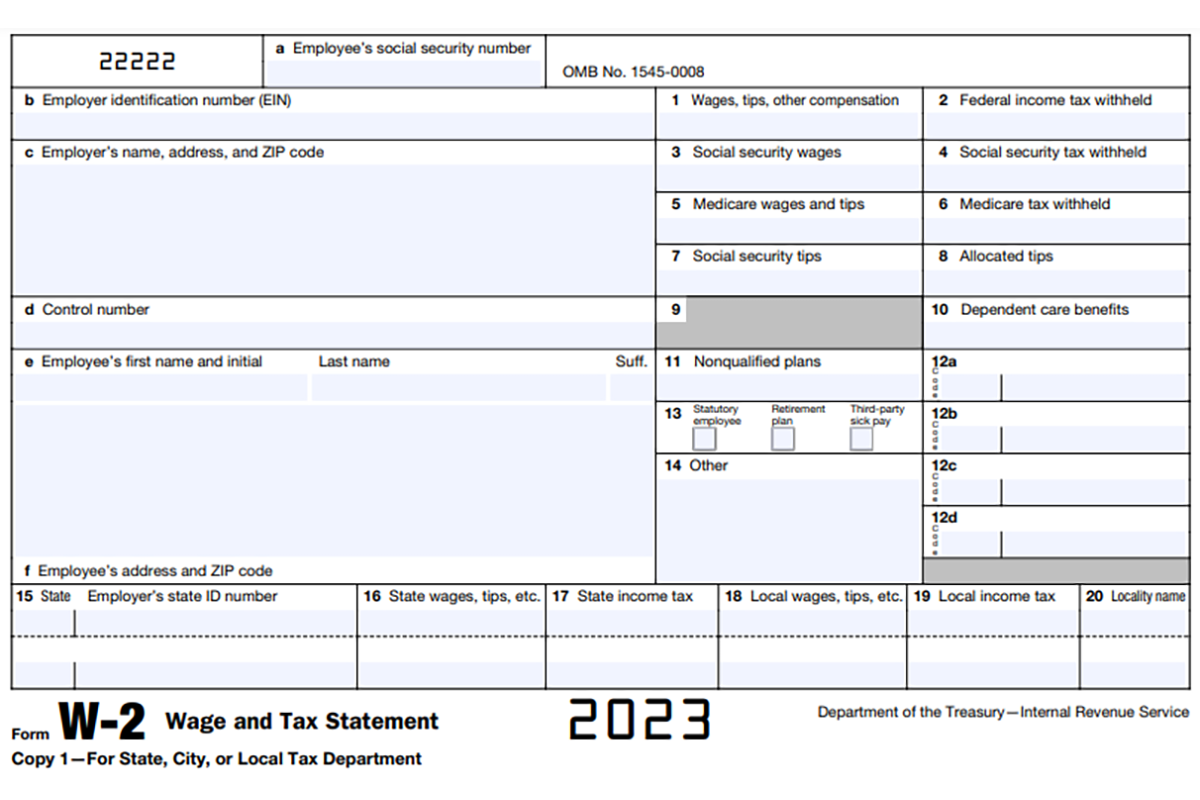
Understanding the boxes on the W-2
Your W-2 contains 20 boxes, but not all will be completed. Here is an explanation of what you will commonly see on your W-2:
Box 1: Wages, tips, other compensation
This is the gross taxable wage amount Penn State Health paid you. This amount includes tips, bonuses, commissions, wages and salaries.
Box 2: Federal income tax withheld
This is the amount of federal income tax withheld from the amount reported in Box 1. Your W-4 was used to determine the tax withholding rate.
Box 3: Social security wages
This is the amount of your earnings, not including tips, that is subject to Social Security tax.
Box 4: Social security tax withheld
This amount is 6.2% of the Social Security wages in box 3 withheld during the year.
Box 5: Medicare wages and tips
This is the total amount of your earnings that is subject to Medicare tax.
Box 6: Medicare tax withheld
This amount is 1.45% of the total Medicare wages in box 5 during the year. If you earn more than $200,000 (single) or $250,000 (married filing jointly), you are also subject to an additional 0.9% Medicare tax.
Box 7: Social security tips
This is any tip income you reported to Penn State Health. For most employees, this box will be empty.
Box 8: Allocated tips
This is tip income allocated to you by Penn State Health. This amount isn’t included in W-2 boxes 1, 3, 5 or 7. For most employees, this box will be empty.
Box 10: Dependent care benefits
This is the total amount paid into your dependent care flexible spending account for the year. Any amount over $5,000 is also included in box 1.
Box 11: Nonqualified plans
This is the total amount distributed to you if you participate in a Penn State Health nonqualified deferred compensation plan.
Box 12: Compensation and benefits
Boxes 12a–d list compensation or benefits by code. The codes include elective deferrals for a 401(k) retirement plan, cost of Penn State Health-sponsored health coverage and taxable cost of group-term life insurance.
Box 13: Retirement plan
This box is checked when an employee is an active retirement plan participant.
Box 14: Other
This box is used to report miscellaneous information, such as state disability insurance taxes withheld, uniform payments or educational assistance payments.
Box 16: State wages, tips, etc.
This is the amount of the wages Penn State Health paid you that is subject to state tax. The amount in box 16 might be higher than the amount shown in box 1. For example, Pennsylvania taxes retirement plan contributions, which are not subject to federal tax.
If you have questions, please email HR Solutions.
If you're having trouble accessing this content, or would like it in another format, please email Penn State Health Marketing & Communications.
